According to Environment and Climate Change Canada, “fourteen tornadoes struck several Ontario communities, namely Barrie, Grand Valley, Orangeville and Tottenham. The Barrie tornado killed eight people. In all, the family of tornadoes injured hundreds of people, destroyed or damaged over 1,000 buildings and killed 12 people, tying it with the Pine Lake, AB tornado in 2000 as the fourth deadliest tornadic day in Canada. The Grand Valley tornado that began near Arthur and moved east to Campbellford is considered one of the longest tracked tornadoes in Canada, travelling over 115 km” (ECCC, 2017).
This tornado was the third and final one to be produced by the “southern supercell” on May 31. It touched down about 7km SSW of Lindsay felling a 200 metre wide swath of trees as it churned ENE toward the Scugog River.
East of the river, it crossed over Highway 35 where it demolished two barns and threw their metal roofs to the east and cut through another wooded area uprooting trees. At Hillhead Corners, the tornado destroyed a log barn, damaged another, and removed the top of a silo on one farm just south of the small hamlet.
Continuing just south of and parrallel to Highway 7, it unroofed another barn about one kilometre west of Reaboro. Skirting the village to the south, the potent tornado instead sliced through an area of trees but also hit another property where a truck camper was turned upside down.
About three kilometre ENE of Reaboro, other rural properties were struck, including a farm where a barn was destroyed, and another nearby on which a number of barns and outbuildings were twisted and stripped of their roofs.
At the south end of Pigeon Lake, tree damage occurred along the north and east sides of Cowans Bay, especially in Emily Provincial Park where damage was extensive.
The tornado persisted ENE for approximately seven kilometre over mainly open areas where it crossed into Peterborough County. It then began to weaken somewhat and ultimately lifted off south of Youngstown on Lake Chemong.
The Forecast
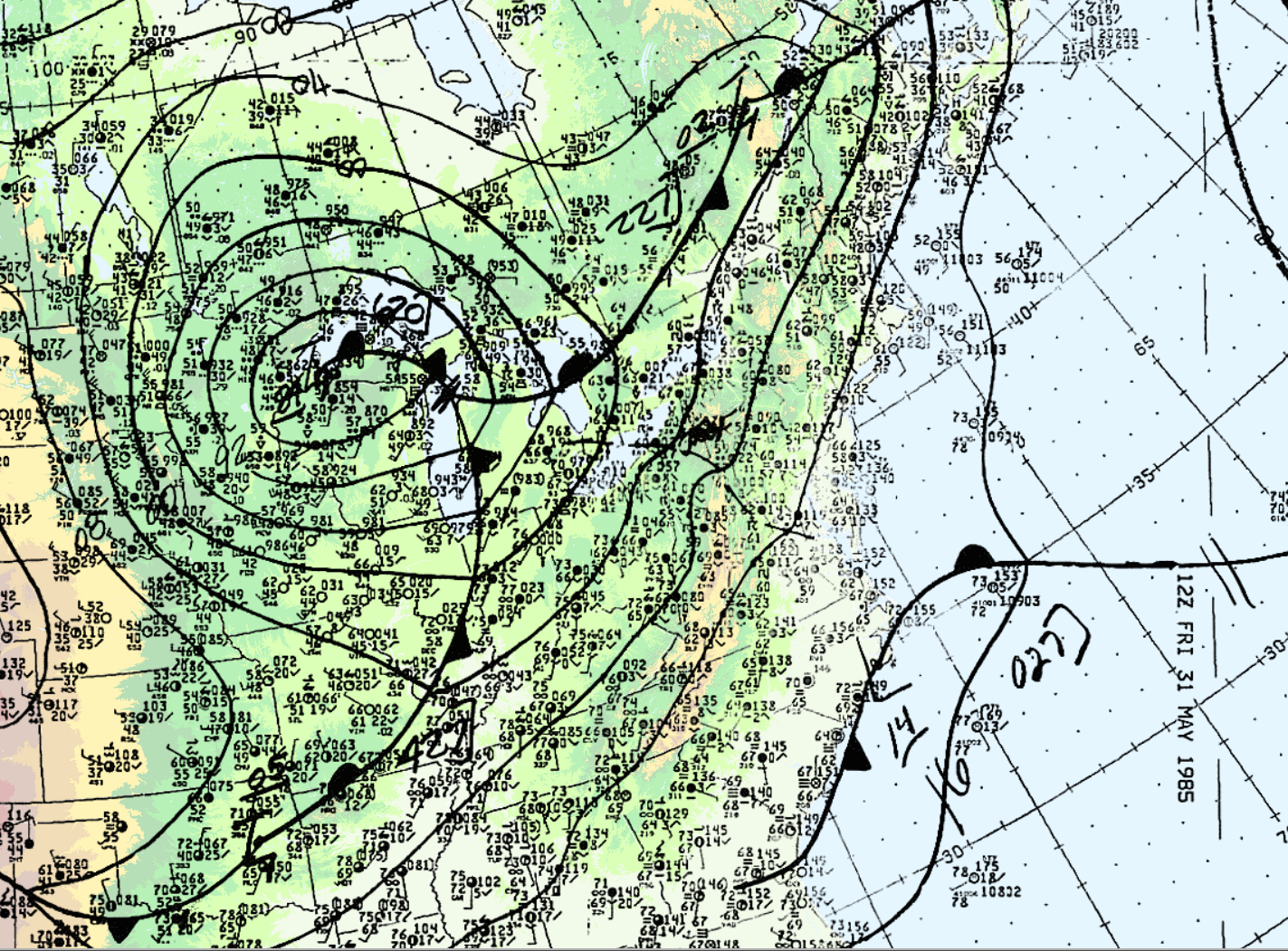
On the morning of May 31, 1985, warm air was advecting northward across Ontario. Figure 1 depicts the surface analysis on the morning of May 31st. In Figure 1, we can see a warm front advecting northward across Ontario and a cold front moving eastward (entering Michigan). The cold front would later provide the trigger for explosive supercell thunderstorm development. According to M. Leduc, O. Jacobsen and B. Greer (1986), “the morning analysis at Environment Canada’s Ontario Weather Centre (OWC) indicated that the thermodynamic and dynamic features necessary for the possible development of severe thunderstorms were present”. As a result, severe weather watches were issued at 2:40 am local time for southern Ontario and extended for all of southern Ontario at 7:00 am, 9:20 am and 1:50 pm, advising the population of potential severe thunderstorm development later in the day (Leduc et al., 1986).
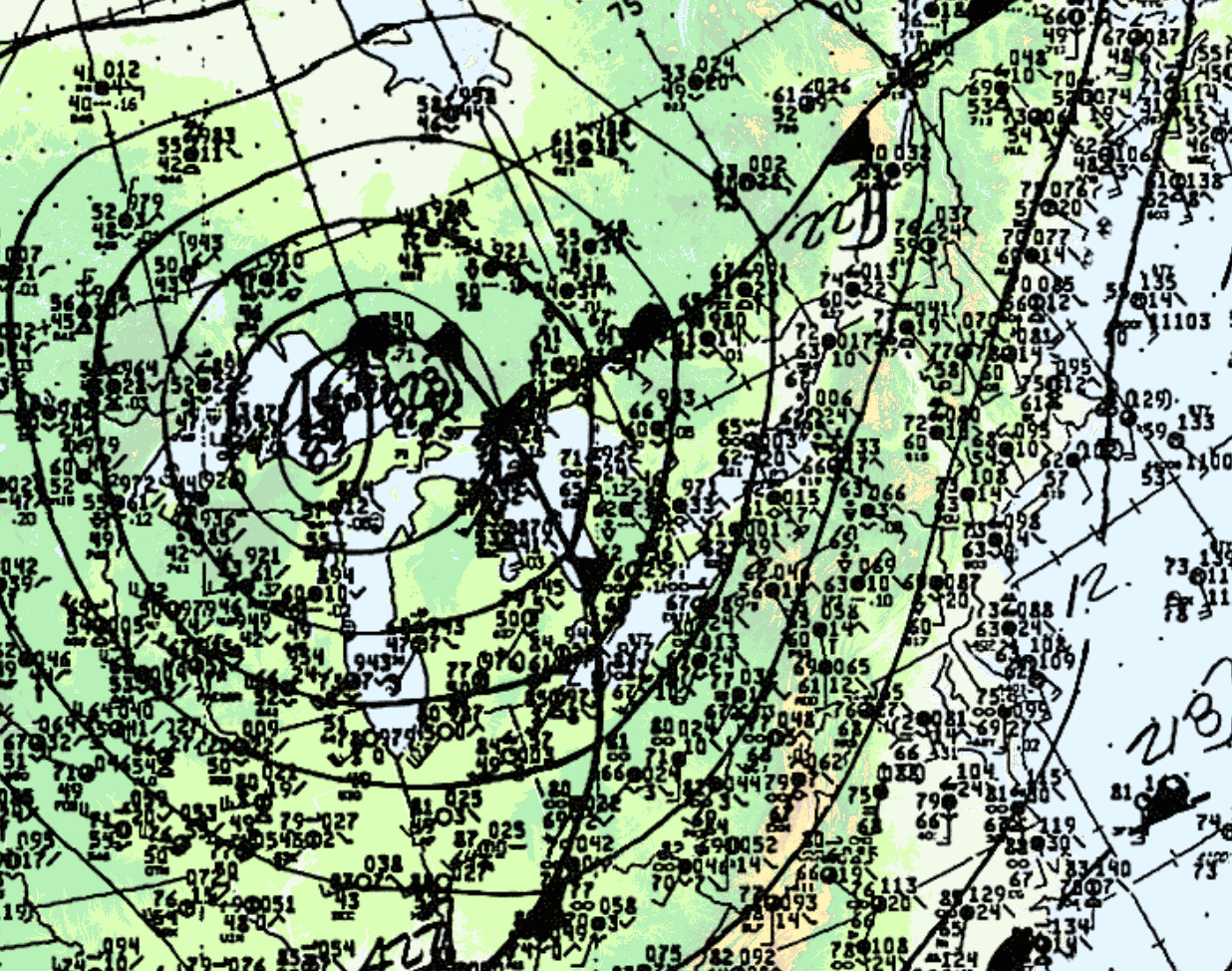
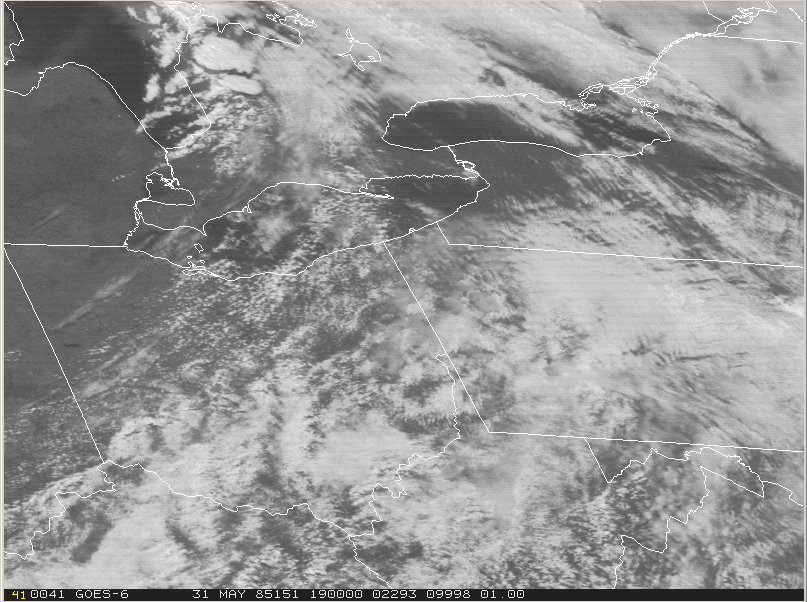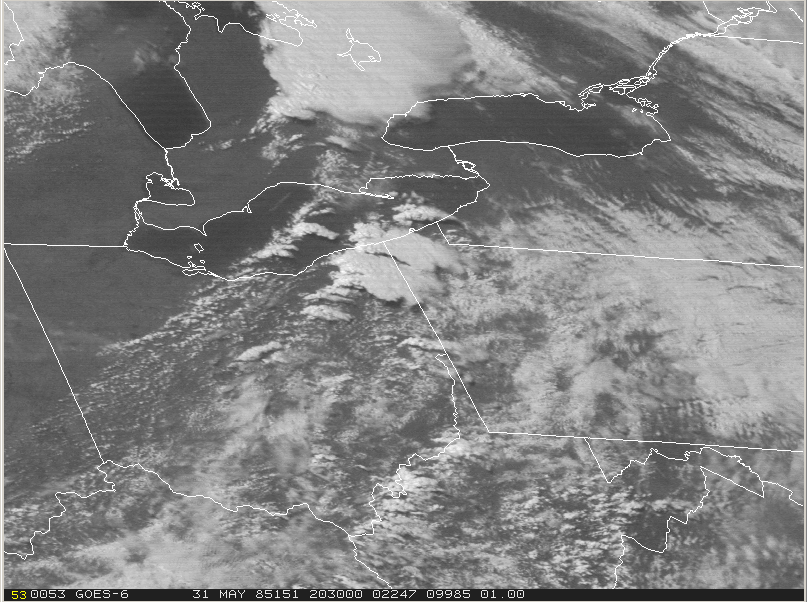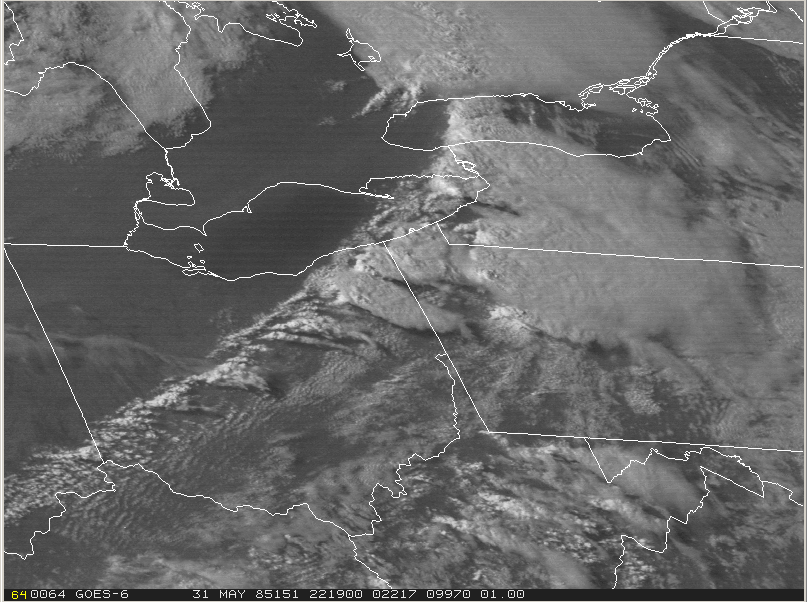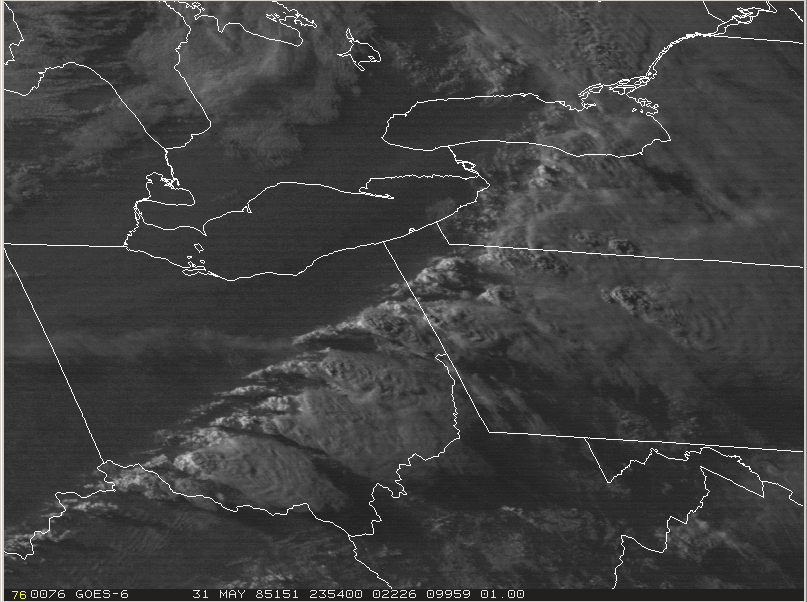
At 18Z (2:00 pm EDT), the cold front was entering Ontario (Figure 2). According to Leduc, et al. (1986), an unseasonably strong low pressure centre tracked across upper Michigan during the morning hours to just north of Sudbury by evening. The visible satellite loop below shows the development and explosive growth of thunderstorms across southern Ontario, Ohio, western Pennsylvania and western New York on the afternoon of May 31st.
At 21Z (5:00 pm EDT), the cold front was in western Ontario (Figure 4).
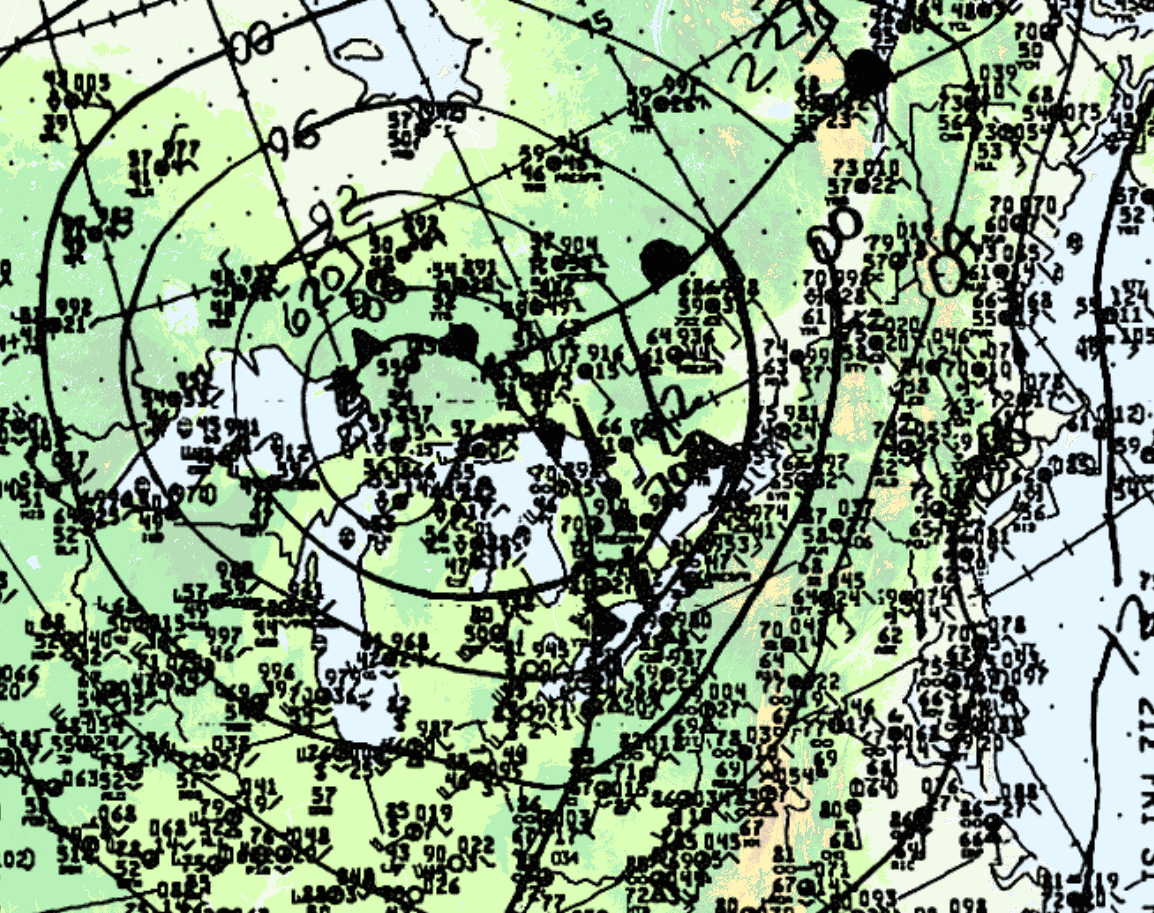
Leduc et al. (1986) notes that the dynamics in place were strong since a sharp cold front (Figure 1, 2 and 4) and an upper trough was crossing Michigan, bringing with it strong westerlies in the upper-levels of the atmosphere.
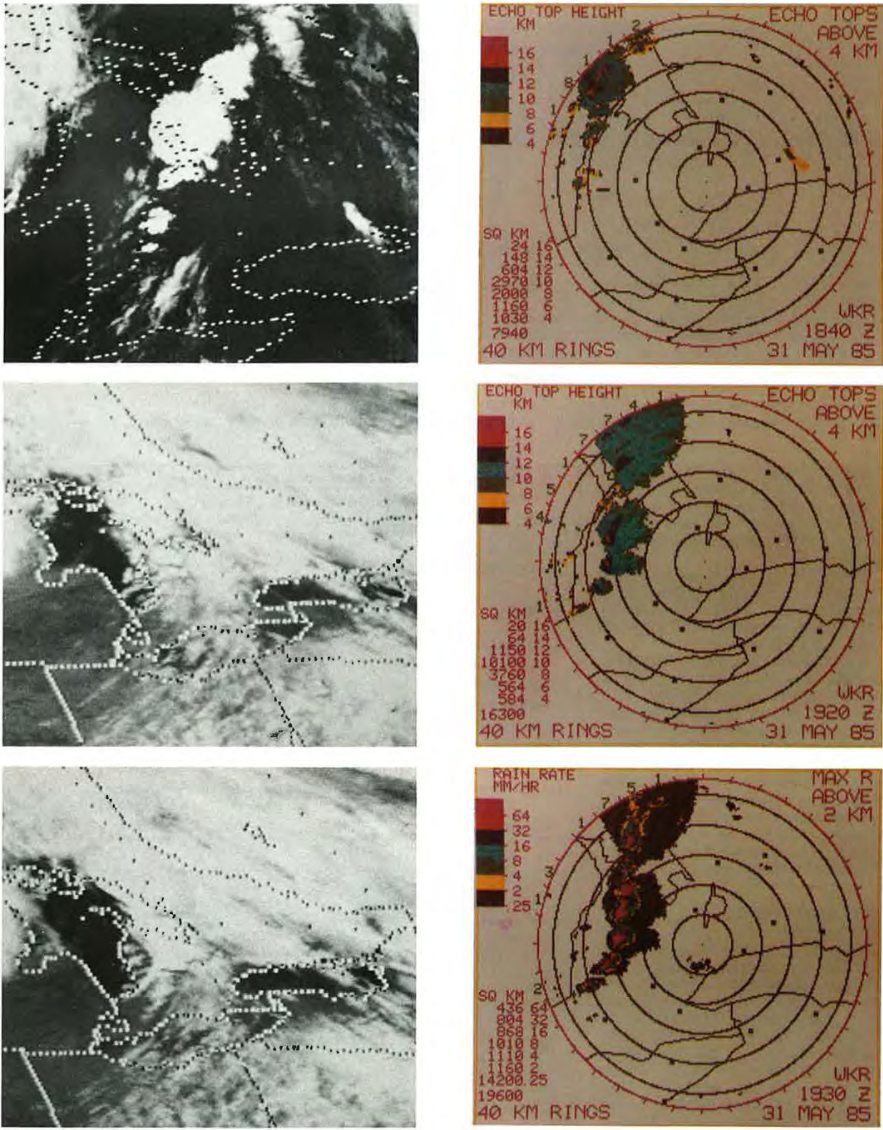
Figure 5 and 6 depict the radar imagery from the King City radar (north of Toronto). At 1:40 pm (local time), radar showed the first thunderstorms developing west and north of the Bruce Peninsula. By 2:20 pm, a line of severe storms was indicated by radar (Figure 5). The first severe thunderstorm warning was issued at 2:25 pm for the Bruce County and Parry Sound District. At 3:15 pm, severe thunderstorm warnings were issued for Huron, Perth, Grey, northern Wellington and northern Waterloo Counties, with the most intense storms being seen from Meaford to Perth County (Leduc et al., 1986). At 4:00 pm, reports of 2-cm hail and very high winds were received at the OWC for the Meaford and Dundalk area. Around 4:00 pm, radar showed a line of severe storms extending from Collingwood to eastern Perth County moving east at 60-70 km/h (Figure 6).
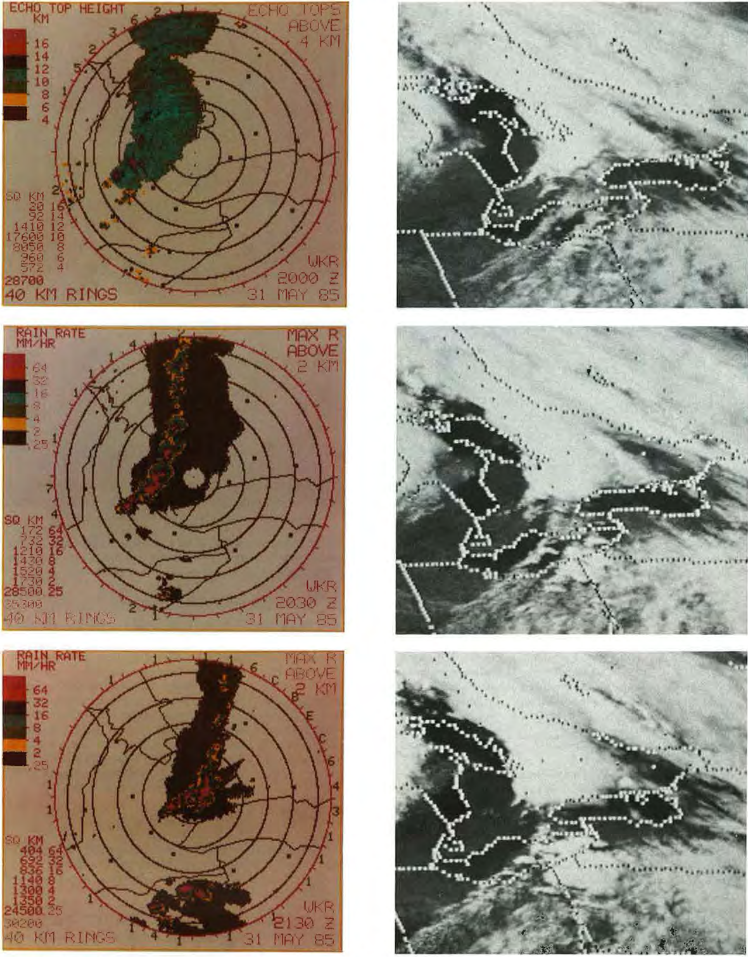
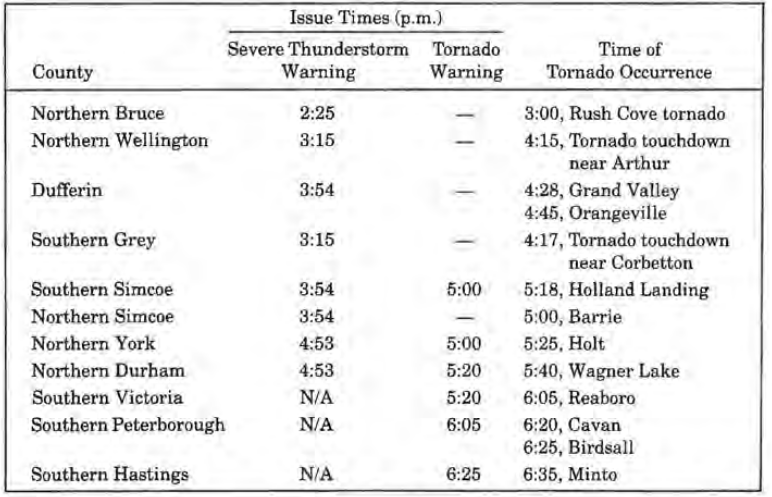
Between 4:20 pm and 4:40 pm, radar showed signs that the southern storms off the squall line were intensifying and therefore warnings were issued at 4:53 pm from Hamilton-Wentworth to Durham and Victoria counties. A tornado warning was issued at 5:00 pm for southern Simcoe, northern Peel and York counties after OWC received reports of a tornado at 5:00 pm and 5:20 pm. At 5:50 pm severe thunderstorm warnings were issued for the Niagara Peninsula. Tornado warnings were extended for southern Durham and Peterborough counties at 6:05 pm and Haliburton, Northumberland, Prince Edward and Hastings counties at 6:25 pm. At 7:00 pm, warnings/watches were cancelled for all regions, except for Haliburton County and east of Oshawa where tornado reports southwest of Peterborough and Rawden Township were received between 6:40 pm and 7:20 pm. A timeline of tornado occurrence, severe thunderstorm warnings and tornado warnings are presented in Table 1 below.
Recap
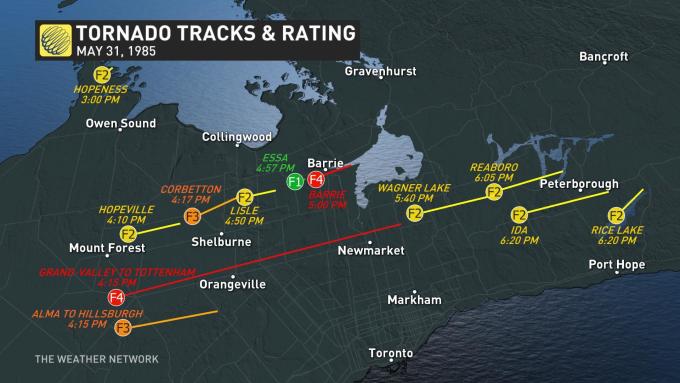
According to ECCC (2018), the Reaboro F2 tornado touched down at 6:05 pm local time southwest of Lindsay, ON and tracked for 31.2 km, moving in a east-northeasterly direction and ending over Chemong Lake. The maximum width of the tornado was not documented. ECCC (2018) did not catalogue any injuries, fatalities or damage associated with this tornado.
Sources
Environment and Climate Change Canada (2017). Top Weather Events of the 20th Century. Retrieved from: https://ec.gc.ca/meteo-weather/default.asp?lang=En&n=6A4A3AC5-1#tab5
NWS
Weather Prediction Center (2017). North American Surface Analysis:
Surface Analysis 12Z Friday May 31, 1985. Retrieved from: https://www.wpc.ncep.noaa.gov/html/sfc2.shtml
National Weather Service (2019). May 31, 1985 Tornado Outbreak: 34th Anniversary. Retrieved from: https://www.weather.gov/ctp/TornadoOutbreak_May311985#Meteorology
M. Leduc, O. Jacobsen and B. Greer (Winter 1986). The “Black Friday” Tornado Outbreak in Ontario. Chinook, 8, 13-18. Retrieved from: cmosarchives.ca/Chinook/ch0801.pdf
The Weather Network (2019). Massive Ontario tornado outbreak marks anniversary. Retrieved from: https://www.theweathernetwork.com/ca/news/article/anniversary-of-the-barrie-tornado-grand-valley-tottenham-may-31-1985-tornado-outbreak
Environment
and Climate Change Canada (2018). Canadian National Tornado
Database: Verified Events (1980-2009) – Public. Retrieved from: http://donnees.ec.gc.ca/data/weather/products/canadian-national-tornado-database-verified-events-1980-2009-public/?lang=en

